HEALTH
What Is Cream Top Milk? Understanding the Natural Goodness
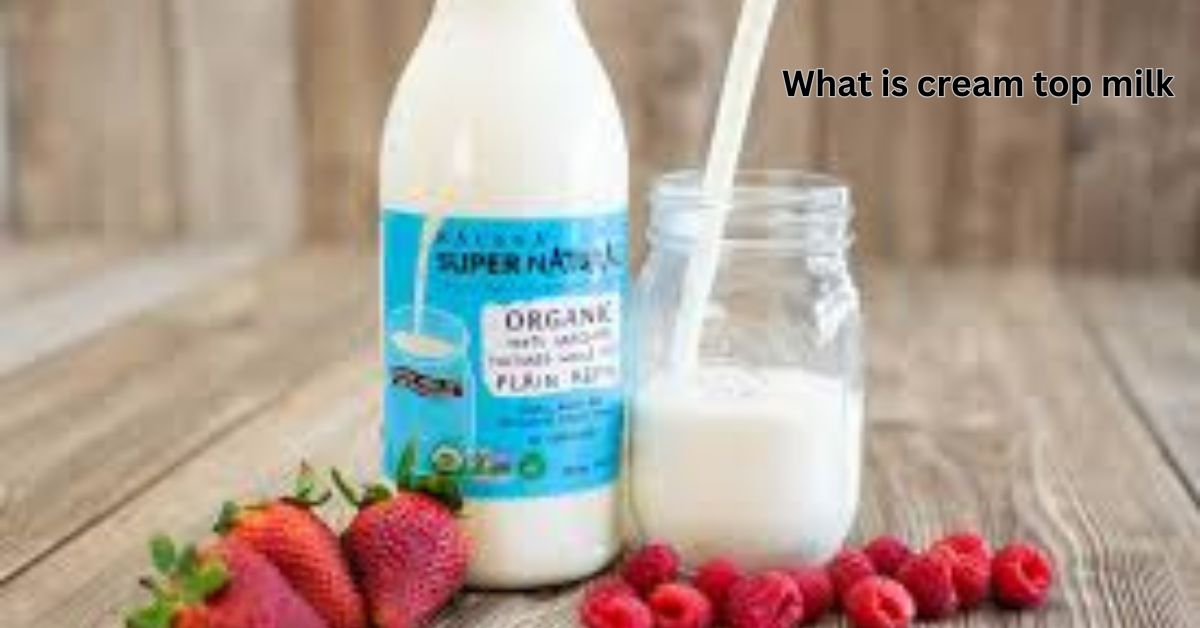

What Is Cream Top Milk’s? Understanding the Natural Goodness
In the world of dairy, there are many options to choose from when it comes to milk. One such option is cream top milk, a natural and wholesome type of milk that has gained popularity in recent years for its rich taste and health benefits. But what exactly is cream top milk’s, and how is it different from the regular milk you may find at the grocery store? In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of cream top milk, its benefits, how it compares to other types of milk’s, and why you might consider adding it to your diet.
What Is Cream Top Milk’s?
Cream top milk’s refers to milk’s that has not undergone homogenization, a process in which the fat molecules are broken down so they can be evenly distributed throughout the liquid. As a result, cream top milk’s retains its natural fat content, and you’ll notice a layer of cream that rises to the top of the milk’s. This layer is a natural concentration of butterfat that provides a richer, creamier texture than regular milk.
Cream top milk’s is typically produced from whole milk’s, and because it is less processed than regular milk, it maintains more of the natural nutrients found in fresh milk’s. Unlike homogenized milk, which has been mechanically processed to prevent the cream from separating, cream top milk’s gives you a glimpse into the natural state of milk, as it appears directly after being milked from cows.
Key Characteristics of Cream Top Milk’s
-
Rich and Creamy: The most noticeable feature of cream top milk’s is the thick layer of cream that forms at the top. This is due to the higher fat content compared to regular milk’s, making it taste richer and creamier.
-
Higher Fat Content: Unlike standard milk’s, which is often skimmed or reduced in fat, cream top milk typically has a higher fat content, generally around 4% or more. The cream that rises to the top is what gives the milk’s its indulgent texture and taste.
-
No Homogenization: Homogenization is the process of breaking down the fat molecules in milk so that they are evenly distributed throughout the liquid. Cream top milk’s is not homogenized, which allows the cream to naturally separate from the milk’s.
-
Natural Nutrients: Because cream top milk is less processed, it retains more of the natural vitamins and minerals found in milk’s, including fat-soluble vitamins like Vitamin A and D.
How Is Cream Top Milk Made?
Cream top milk is made in a straightforward manner, involving minimal processing. Here’s an overview of the process:
1. Milk Collection
The process begins by collecting fresh milk from dairy cows. The milk’s is typically taken directly from the cow and transported to the dairy for processing.
2. Separation of Cream
Once the milk’s reaches the dairy, it is allowed to sit for a while. Over time, the cream, which is made up of fat, naturally rises to the top of the milk’s. This is a natural process and doesn’t require any special equipment. The result is a layer of cream on top of the milk’s, with the lower portion being the liquid milk.
3. Packaging and Distribution
Once the cream has separated, the milk’s is carefully bottled or packaged. The cream top milk’s is typically sold as-is, without the need for further processing like homogenization, allowing customers to experience the milk in its natural form.
4. Optional: Cream Removal
In some cases, manufacturers may choose to remove a portion of the cream from the milk before packaging it. However, unlike skim or low-fat milk, cream top milk’s retains a significant amount of cream, so it’s still much richer than regular milk.
Benefits of Cream Top Milk’s
Cream top milk’s is often touted for its numerous health benefits, particularly due to its higher fat content and natural processing. Let’s dive into the benefits that make this milk so appealing to health-conscious consumers.
1. Better Taste and Texture
One of the biggest draws of cream top milk’s is its rich, creamy taste. The higher fat content gives it a thicker consistency, which many people find more satisfying and indulgent. Whether used in coffee, baking, or enjoyed on its own, cream top milk adds a luxurious texture and flavor that regular milk can’t match.
2. More Nutrients
Because cream top milk’s is less processed, it retains more of the natural nutrients found in whole milk’s. The fat in milk plays an important role in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamins A, D, and E. Therefore, drinking cream top milk’s may offer more nutritional value compared to skimmed or homogenized milk.
Additionally, cream top milk’s contains healthy fats that can be beneficial for the body. These fats provide energy and help support the absorption of essential nutrients, and they are also a key part of a balanced diet when consumed in moderation.
3. Supports Digestive Health
The natural fats and proteins found in cream top milk’s are more easily digested by some individuals, particularly those who may have difficulty processing highly processed dairy products. Some people find that cream top milk causes less bloating or discomfort compared to homogenized milk’s.
4. No Added Sugar or Artificial Ingredients
Unlike some commercial milk’s products that may contain added sugars, preservatives, or artificial ingredients, cream top milk typically has none of these additives. This makes it a cleaner, more natural choice for individuals who are concerned about the purity of the food they consume.
5. Rich in Healthy Fats
Cream top milk’s contains healthy saturated fats, which play an important role in supporting brain health, hormone production, and the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. While it’s important to moderate fat intake, these fats are still necessary for overall health and well-being.
Cream Top Milk’s vs. Regular Milk
To understand the key differences between cream top milk and regular milk, let’s compare them across several factors:
| Factor | Cream Top Milk’s | Regular Milk |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Content | Higher (around 4% or more) | Varies (1% to 2% fat for reduced-fat; skim milk has almost no fat) |
| Homogenization | Not homogenized; cream rises to the top | Homogenized for uniform texture |
| Taste and Texture | Rich, creamy, thicker texture | Lighter, thinner texture |
| Nutrient Retention | Retains more fat-soluble vitamins | Less retention of nutrients due to processing |
| Processing | Minimal processing, more natural | Processed for consistency and shelf-life |
As you can see, cream top milk’s stands out because of its richer texture, higher fat content, and minimal processing compared to regular milk.
Is Cream Top Milk Right for You?
Cream top milk’s can be a great addition to your diet, but it may not be suitable for everyone. Here are a few factors to consider when deciding if this type of milk is the right choice for you:
- Dietary Preferences: If you’re looking for a milk’s that is creamy and rich in flavor, cream top milk might be an excellent option. However, if you’re on a low-fat diet, you may prefer skim milk or low-fat alternatives.
- Health Considerations: Some people may be concerned about the higher fat content in cream top milk. While healthy fats are important, it’s still necessary to moderate your intake if you’re watching your calorie or fat consumption.
- Lactose Sensitivity: If you’re lactose intolerant, you may want to explore lactose-free options, as cream top milk contains the same amount of lactose as regular milk.
- Flavor Preference: If you prefer a lighter taste in your milk or are used to the texture of regular, homogenized milk, cream top milk might feel too rich or heavy.
How to Use Cream Top Milk
Cream top milk can be used in a variety of ways, from drinking it straight to adding it to recipes. Here are some ways to enjoy it:
- In Coffee or Tea: Add cream top milk’s to your morning coffee or tea for a rich, creamy texture that enhances the flavor.
- In Baking: Use cream top milk’s in baking recipes like cakes, muffins, or pancakes for added moisture and richness.
- As a Drink: Enjoy it chilled, straight from the bottle, or with a dash of vanilla for a natural, delicious treat.
- In Smoothies: Blend it into smoothies for a creamy base that pairs well with fruits and other ingredients.
Conclusion
Cream top milk’s is a natural, less processed option that offers a richer, creamier taste compared to regular milk. With its higher fat content and more nutrients, it provides a wholesome alternative for those looking to enjoy the full goodness of milk’s without the additives and processing found in many commercial dairy products. Whether you enjoy it in your morning coffee, as part of a recipe, or simply as a refreshing drink, cream top milk can be a delightful addition to your diet. If you’re seeking a more natural, indulgent milk option, cream top milk’s may just be the perfect choice.
HEALTH
How to Choose the Besto Pesto for Pasta & More

Pesto isn’t just a sauce; it’s a story of tradition, taste, and versatility. Whether you want to toss it with pasta, spread it on bread, or swirl it into soup, pesto delivers rich, bold flavors. But with so many besto pesto brands out there, shoppers often struggle with one question: Which pesto should I buy?
One food lover recently shared online: “I tried five different jars last month, and only one actually tasted like fresh basil and Parmesan. The rest felt too oily or bland.” This sums up the common frustration—picking the right pesto is tricky.
That’s where besto pesto comes into play. Let’s explore how it compares to authentic Italian pesto, what to look for in healthy pesto options, and why reviews matter in 2025.
Best Pesto Brands in 2025
Choosing from the best pesto brands isn’t just about popularity. It’s about ingredient sourcing, taste consistency, and health-conscious production.
What Sets the Best Brands Apart?
- Fresh basil quality – Authentic Genovese basil makes all the difference.
- Cheese choice – Parmigiano-Reggiano vs. Grana Padano.
- Nuts – Pine nuts are traditional, but walnuts and cashews offer affordable twists.
- Oils – Extra virgin olive oil remains the gold standard.
Some leading brands in 2025 emphasize organic sourcing, while others keep prices competitive by offering store-bought pesto in family-friendly jars.
Authentic Italian Pesto: Tradition That Never Fades
When people think of authentic Italian pesto, they picture traditional basil pesto from Genoa. This style—known as Genovese pesto—dates back centuries and follows strict ingredient rules.
Key Characteristics of Genovese Pesto:
- Genovese DOP basil
- Extra virgin olive oil from Liguria
- Parmigiano-Reggiano and Pecorino cheese blend
- Pine nuts and garlic
Imported jars of authentic Italian pesto remain premium but are increasingly available worldwide. If you’re chasing tradition, this is the benchmark.
Homemade Pesto Alternatives
Not everyone wants a jar. Many people prefer homemade pesto alternatives because they control freshness, oil levels, and nut variations.
Why Go Homemade?
- Control salt and oil levels
- Customize with kale, spinach, or arugula
- Save money with nut substitutions
- Freeze for later use
That said, besto pesto jars are designed to mimic that homemade quality, which is why they’re so appealing to busy households.
Pesto Sauce Recipes You’ll Love
If you buy besto pesto, you’ll want creative ways to use it beyond pasta.
Popular Pesto Uses in 2025:
- Toss with roasted veggies
- Spread on sandwiches and wraps
- Drizzle on grilled chicken or salmon
- Swirl into soups or risottos
- Mix into scrambled eggs
For adventurous cooks, pesto sauce recipes now include blends with sun-dried tomatoes, lemon zest, and even avocado.
Organic Pesto: A Health-Conscious Trend
The demand for organic pesto continues to rise in 2025. Shoppers want fewer preservatives, eco-friendly farming, and pesticide-free basil.
Benefits of Organic Pesto:
- Cleaner label with recognizable ingredients
- Supports sustainable farming
- Often packaged in eco-conscious jars
Besto pesto has carved a niche by appealing to this health-driven crowd, balancing taste with sustainability.
Jarred Pesto Reviews: What Buyers Are Saying
Nothing guides purchasing decisions like real feedback. Jarred pesto reviews in 2025 highlight a few key factors:
- Texture consistency (not too oily, not too thick)
- Authenticity of flavor
- Price vs. portion size
- Shelf life after opening
Some buyers note that store-bought pesto can be salty, so reading labels remains essential.
Store-Bought Pesto vs. Homemade: Which Wins?
Here’s a quick comparison to help you decide between store-bought pesto and making your own.
| Feature | Store-Bought Pesto | Homemade Pesto |
|---|---|---|
| Convenience | Ready anytime | Takes prep time |
| Flavor Consistency | Same each jar | Depends on fresh ingredients |
| Customization | Limited | Fully customizable |
| Cost | Moderate | Can be cheaper |
| Shelf Life | Weeks (sealed) | Days (fresh) |
For many busy families, besto pesto balances the best of both worlds.
Traditional Basil Pesto: The Classic Base
The foundation of most brands remains traditional basil pesto. While creative blends are growing, nothing beats that bright green flavor paired with Parmesan and pine nuts.
Besto pesto often markets its jarred version as “like Nonna made it.” That branding resonates with buyers craving tradition in a modern package.
Genovese Pesto: Protected and Prestigious
Genovese pesto holds DOP (Protected Designation of Origin) status in Italy, ensuring authenticity. Not every jar labeled “pesto” qualifies. True Genovese pesto has strict rules about basil, cheese, and olive oil origin.
When buying besto pesto, check if the label emphasizes authenticity or Genovese-style roots.
Healthy Pesto Options in 2025
Modern consumers don’t just want tasty food—they want healthier choices. Healthy pesto options now include:
Lower-sodium jars
Vegan pesto (using nutritional yeast instead of cheese)
Nut-free pesto for allergy concerns
Low-oil versions for calorie-conscious eaters
Besto pesto has adapted by offering lighter variations without losing its signature flavor.
Real-Life Example: A Busy Parent’s Perspective
One parent shared: “I love cooking, but after work I barely have time. Besto pesto saves me. My kids think dinner is special even when I just toss it with pasta. It’s my weeknight hero.”
This shows how store-bought pesto fits into everyday life—not as a compromise, but as a smart solution.
FAQ’s
What is Besto Pesto made of?
Besto pesto usually includes basil, extra virgin olive oil, Parmesan cheese, pine nuts (or alternatives), and garlic. Some variations are vegan or organic.
Is Besto Pesto healthy?
Yes, especially if you choose healthy pesto options. It’s nutrient-dense but can be high in calories, so moderation is key.
How does Besto Pesto compare to homemade pesto?
While homemade offers customization, jarred pesto reviews praise Besto Pesto for consistency, convenience, and authentic taste.
Can I freeze Besto Pesto?
Yes. Like most store-bought pesto, freezing helps preserve flavor and texture for longer storage.
Final Thoughts
From authentic Italian pesto roots to modern organic pesto trends, the pesto market is booming in 2025. Whether you want fluffy homemade pesto alternatives, healthy pesto options, or simply a reliable jar, besto pesto delivers quality and convenience.
HEALTH
How Patient Check-In Technology Is Simplifying Healthcare

Healthcare facilities increasingly adopt digital patient check-in systems to enhance efficiency, reduce administrative burdens, and improve patient experiences. These self-service kiosks and online platforms allow patients to update personal information, verify insurance, and complete forms quickly, minimizing wait times and reducing paperwork. By automating repetitive tasks, staff can focus more on patient care, which boosts morale and reduces costly human errors. The technology also supports greater accuracy in record-keeping, helping ensure compliance with healthcare regulations. The streamlined process reduces stress and creates a smoother journey from arrival to treatment for patients. Facilities benefit from faster throughput, improved data management, and the ability to allocate staff resources better. As healthcare demand grows and workforce shortages persist, efficient check-in solutions have become essential in meeting operational needs and patient expectations, making the care experience more seamless, accurate, and satisfying for everyone involved.
Introduction
The healthcare industry faces mounting pressures from rising patient volumes and ongoing staffing shortages, making operational improvements more critical than ever. Technology-driven tools are emerging as key allies in bridging service gaps and enhancing overall care delivery. In an era where efficiency and patient satisfaction are paramount, healthcare providers are turning to modern solutions to streamline administrative tasks and improve patient journeys. One of the most significant advancements in recent years is the adoption of check-in kiosks for patients, which are transforming how patients engage with healthcare facilities from the moment they arrive. These digital solutions offer a seamless, self-service alternative to traditional paper-based and manual check-in processes, addressing common pain points such as long wait times and paperwork overload.
By digitizing the check-in experience, facilities can enhance data accuracy, expedite patient flow, and reduce staff administrative workload. As more healthcare organizations implement these innovations, patients and providers are discovering the tangible benefits they bring, including improved compliance, better information management, and a more welcoming atmosphere for all visitors. The integration of check-in kiosks for patients is just one example of how technology is making healthcare more accessible, personalized, and efficient.
The Evolution of Patient Check-In
For decades, patient check-in at clinics and hospitals relied on manual steps: forms were filled out by hand, identification and insurance cards were presented at the front desk, and staff would collect and enter this information. This approach created bottlenecks at busy reception areas and increased the risk of errors and miscommunication. It became clear that a more efficient and patient-friendly system was needed, sparking the shift to digital alternatives.
The rise of digital check-in solutions began with simple electronic forms and has rapidly evolved to include self-service kiosks, tablet-based registration, and mobile check-in through dedicated apps or online portals. These platforms empower patients to update their records, review consent forms, and verify insurance benefits with minimal assistance, often before arriving at the facility. The result is a more streamlined process that benefits patients and healthcare providers alike.

Benefits of Digital Check-In Systems
- Reduced Wait Times: Digital systems let patients handle paperwork and updates in advance, slashing the time spent in waiting rooms and keeping schedules running on time.
- Enhanced Data Accuracy: Patients directly entering their information significantly reduces transcription mistakes. Digital checks for completeness and legibility further minimize clerical errors common with paper forms.
- Improved Patient Satisfaction: Automated, user-friendly interfaces create smoother, more predictable experiences, reducing frustration and anxiety associated with lengthy check-in queues.
- Operational Efficiency: When administrative staff are liberated from repetitive data entry and paperwork, they can focus on higher-value interactions and more complex patient needs.
Challenges in Implementing Check-In Technology
The path to modernizing check-in procedures is not without its obstacles. Implementing new technology presents notable challenges:
- Cost Implications: Rolling out digital check-in options—especially check-in kiosks—can be costly. Smaller practices may struggle to justify the upfront investment, even with long-term efficiency gains.
- Staff Training: Successful adoption depends on well-trained staff who can troubleshoot issues and help patients use new tools, fostering a smooth integration into daily routines.
- Patient Adaptation: While many patients embrace digital options, older adults or those with limited digital literacy may feel overwhelmed. A compassionate, flexible approach to onboarding is essential to ensure no one feels left behind.
Real-World Examples of Successful Implementation
Many healthcare organizations have demonstrated the positive impact of digital check-in technologies.
- NYU Langone Health: This renowned facility introduced Amazon’s biometric palm scanning technology to provide secure, touchless patient check-in. The move has streamlined identity verification and enhanced privacy and convenience.
- Maidstone and Tunbridge Wells NHS Trust: By implementing TeleTracking’s cloud-based patient flow technology, this UK hospital system reduced emergency department wait times by over an hour per patient and achieved significant operational savings.
Future Trends in Patient Check-In Technology
Healthcare check-in technology is rapidly evolving, and several emerging trends are set to define its future:
- Biometric Authentication: Palm scans, facial recognition, and fingerprints streamline identification while bolstering security.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-driven systems promise to predict patient flow, optimize appointment scheduling, and personalize the check-in process for each visitor.
- Integration with Electronic Health Records (EHR): Seamless synchronization of check-in data with health records ensures clinicians have real-time, accurate information for better care coordination.
Technology like this is reshaping what patients expect from their visits, offering greater convenience, efficiency, and peace of mind. As healthcare facilities continue to invest in digital innovations, they position themselves to meet rising expectations and adapt to future advances with agility.
Ultimately, patient check-in technology—especially solutions such as check-in kiosks—represents a leap forward in making healthcare more responsive, efficient, and patient-centric. As the landscape evolves, these tools will be essential for delivering high-quality, modern care while keeping patient engagement at the heart of every interaction.
HEALTH
Building Futures: Career Paths with IU Health

Building Futures Indiana University Health, commonly known as IU Health, is synonymous with world-class caregiving, robust career advancement, and a culture deeply rooted in professional development. As the largest nonprofit healthcare system in Indiana, it offers a diverse range of roles—from nursing and physician positions to allied health, administrative, and patient care support disciplines. Those drawn to IU Health find themselves in an environment that values work-life balance, tuition reimbursement, and Magnet‑recognized excellence, all while serving communities across the Hoosier State.
A System That Supports Every Stage of Your Career
When you join IU Health, you become part of a vast network—comprising 16 hospitals and more than 38,000 employees—backed by a partnership with the Indiana University School of Medicine . Known for its leadership in academic medicine, IU Health offers opportunities across specialties from critical care nursing to advanced provider roles like Certified Nurse Anesthetist (CRNA). Whether you begin as a medical assistant, step into telemetry, or pursue a position in respiratory therapy, the system is built for upward mobility.
Every position—from entry-level patient care support roles to seasoned healthcare management tracks—features structured training and clear career pathways. For example, the patient care support team works bedside in one of IU Health’s 15 hospitals or community centers and can leverage bridge programs to transition into nursing or allied health roles
Comprehensive Benefits That Empower Staff
IU Health understands that well-being and financial stability are fundamental to long-term satisfaction. They provide:
-
Market-competitive compensation, including up to a 4% 401(k) match with immediate vesting, plus potential additional contributions based on performance
-
Health, dental, and vision insurance, with HSA/FSA options and a wellness incentive program offering up to $1,040 annually
-
Paid parental leave, long-term disability insurance, and bereavement support .
-
Tuition assistance programs, including full tuition reimbursement up to annual limits, qualified certification funding, and eligibility for Public Service Loan Forgiveness
These benefits are designed to support employees through life transitions—from growing families to career advancement—reinforcing IU Health’s commitment to holistic employee care.
Magnet Recognition & Professional Governance in Nursing
IU Health’s nursing division is a pillar of its excellence. Every facility holds either Magnet recognition or ANCC’s Pathway to Excellence® accreditation, hallmark distinctions of superior patient care and nursing leadership Collectively, over 9,000 nurses operate under a professional governance model. This setup promotes shared accountability, evidence-based practice, and decision-making rooted in frontline experience
Nurse career options range from Neonatal ICU (NICU) and oncology to flight nursing and clinical informatics, each offering specialized tracks with ongoing training and clear growth paths. The robust emphasis on professional governance nurtures a culture of continuous improvement and clinical excellence.
Specialist Roles & Education-Focused Workforce
Beyond nurses, IU Health attracts a wide range of allied health professionals and clinical educators. Positions such as Certified Genetic Counselors, Anesthesiologist Assistants, and Clinical Laboratory Scientists are integral to its mission . These roles often involve interdisciplinary teams, complex patient pathways, and opportunities for mentoring in both clinical and academic settings.
IU Health also partners with Indiana University campuses, notably in the IU School of Nursing and School of Medicine, creating synergy between workforce training, research programs, and patient care As a result, professionals—especially those involved in healthcare management—find themselves at the cutting edge of health administration, population health, and academic medicine, supported by graduate fellowships and institutional leadership development opportunities.
Indiana’s Growing Healthcare Economy & Impact
Operating within Indiana—a state with a $63 billion life sciences sector and a booming healthcare job market—IU Health plays a pivotal role Its reach extends beyond Indianapolis across communities that are home to renowned facilities such as Riley Children’s Hospital, a Level I pediatric trauma center, and Ball Memorial Hospital, a teaching hospital in Muncie
These campuses offer a broad spectrum of employee experiences—from rural community hospital nursing to leadership roles in tertiary medical centers. This ensures that every IU Health employee can find both challenge and satisfaction in environments that best suit their professional and personal goals.
FAQs
Q1: What type of benefits can I expect as a new nurse at IU Health?
You’ll access comprehensive medical, dental, and vision plans with HSA/FSA options, wellness incentives, tuition reimbursement, paid parental leave, long-term disability coverage, and a 401(k) match of up to 4% with immediate vesting
Q2: Does IU Health support career growth for non-clinical staff?
Absolutely. IU Health offers clear promotion pathways, certification support, tuition reimbursement, and leadership development programs—even for those in administrative, IT, or healthcare management roles .
Q3: What makes Magnet Recognition important at IU Health?
Magnet designation recognizes excellence in patient-centered care and nursing leadership. It means nurses work under a framework that fosters collaboration, continuing education, and accountability, contributing to high quality outcomes
Q4: Are there opportunities for part-time or flexible schedules?
Yes. Many roles at IU Health, especially in patient care support and nursing, are available in part-time and per diem formats. They also support flexible PTO policies and work-life integration initiatives .
Conclusion
Choosing a career with IU Health means more than landing a job—it’s about joining a mission-driven community that values patient wellness, employee development, and academic excellence. From frontline patient support roles to advanced practitioner and healthcare leadership positions, IU Health offers purpose-driven work, robust educational benefits, and a chance to make a meaningful impact.
-

 GENERAL8 months ago
GENERAL8 months agoClassroom6x: Revolutionizing the Future of Learning
-

 ENTERTAINMENT8 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT8 months agoUnveiling the Mystery of Kashito_Toto: A Digital Frontier
-

 TECHNOLOGY8 months ago
TECHNOLOGY8 months agoUnlocking the Power of SSIS 816: A New Era in Data Integration
-

 TECHNOLOGY8 months ago
TECHNOLOGY8 months agoUnlocking the Mystery of Vy6ys: A Hidden Gem
-

 GENERAL8 months ago
GENERAL8 months agoUnraveling Time: What Hour Was It 8 Hours Ago?
-

 GENERAL8 months ago
GENERAL8 months agoQuid Pro Quo Harassment: What It Is and Why It Matters
-

 BUSNIESS8 months ago
BUSNIESS8 months agoWhat Does ‘In Transit’ Mean? Understanding Shipment Status
-
 BUSNIESS8 months ago
BUSNIESS8 months agoUnderstanding Sell in Trade Locker: A Key to Smart Trading


