GENERAL
What is a fortunate swimming bird

What is a Fortunate Swimming Bird? Exploring the Wonders of Aquatic Birds
Birds are diverse creatures, with each species exhibiting unique behaviors and characteristics that set them apart from one another. Some birds fly gracefully through the air, while others are known for their remarkable swimming skills. Among these swimming birds, there exists a special category known as the “fortunate swimming bird.” But what exactly does this term mean, and what makes these birds so unique? In this article, we will delve into the concept of a fortunate swimming bird, highlighting their behaviors, characteristics, and the environments they thrive in.
Understanding the Concept of a Fortunate Swimming Bird
A “fortunate swimming bird” is not a formal term in ornithology, but rather a descriptive expression that refers to birds that are well-suited for life in aquatic environments. These birds are fortunate in the sense that they are able to seamlessly navigate both air and water, making them well-adapted to a variety of ecosystems. They are equipped with specialized traits that allow them to swim, dive, and hunt effectively in water while still maintaining their abilities to fly or glide.
Common Characteristics of Swimming Birds
Swimming birds share certain characteristics that enable them to thrive in both water and air. These traits include:
1. Webbed Feet or Specialized Feet
One of the key adaptations of swimming birds is their webbed feet. The webbing acts like a paddle, helping them move efficiently through the water. For example, ducks, swans, and geese have webbed feet that allow them to swim gracefully across lakes and ponds. Other birds, like penguins, have evolved specialized flipper-like wings that function as efficient paddles for swimming.
2. Streamlined Bodies
Fortunate swimming birds are typically built with streamlined bodies that reduce water resistance. This makes it easier for them to glide through water with minimal effort. Their bodies are often sleek and compact, allowing them to move swiftly beneath the surface. This streamlined design is a key characteristic of birds such as loons and auks.
3. Waterproof Feathers
In order to stay dry and buoyant while swimming, many aquatic birds have waterproof feathers. Birds like ducks and puffins produce natural oils from glands near their tails, which coat their feathers and create a waterproof barrier. This allows them to dive into the water without getting weighed down by wet feathers.
4. Diving and Hunting Skills
Many fortunate swimming birds are also exceptional divers, using their swimming skills to hunt for food underwater. For example, pelicans are known for their dramatic diving skills, plunging into the water to catch fish. Similarly, cormorants dive to depths in search of prey, using their webbed feet and streamlined bodies to move quickly through the water.
5. Adaptability to Diverse Environments
Fortunate swimming birds are incredibly adaptable. Whether they inhabit freshwater lakes, coastal shores, or icy polar waters, these birds are equipped to thrive in a variety of environments. Their ability to transition between air and water makes them highly versatile and resilient to changes in their habitats.
Examples of Fortunate Swimming Birds
There are several species of birds that fall under the category of fortunate swimming birds. Each of these species has unique traits that allow them to thrive in their aquatic environments. Let’s look at some examples:
1. Ducks
Ducks are perhaps the most iconic example of swimming birds. With their webbed feet and waterproof feathers, ducks are perfectly adapted to life in the water. They are found in a variety of habitats, including freshwater lakes, rivers, and marshes. Ducks are capable of both swimming and flying, which allows them to migrate over long distances to find food or suitable breeding grounds. Their ability to dive for food, such as aquatic plants, small fish, and invertebrates, makes them excellent swimmers.
2. Penguins
Penguins are one of the most famous examples of swimming birds. Unlike ducks, penguins are flightless, but they are exceptional swimmers. Penguins have evolved flipper-like wings that are used for propulsion in the water, allowing them to “fly” underwater at remarkable speeds. These birds are found primarily in the Southern Hemisphere, particularly in cold, icy environments like Antarctica. Their thick, insulating feathers and layer of fat help them survive in frigid temperatures. Penguins primarily feed on fish and krill, which they catch while swimming and diving.
3. Cormorants
Cormorants are another group of aquatic birds that possess impressive swimming abilities. These birds are found in both freshwater and coastal environments and are known for their diving prowess. Cormorants have long, slender bodies and webbed feet, which enable them to dive deeply and swim efficiently. They hunt for fish by diving underwater and using their powerful swimming abilities to chase down their prey. Cormorants often dry their wings after swimming, as their feathers are not entirely waterproof.
4. Swans
Swans are large, graceful waterfowl that are well-suited for both swimming and flying. With their long necks and elegant appearance, swans are often seen gliding across ponds, lakes, and rivers. Their webbed feet help them paddle through the water, while their strong wings allow them to take flight. Swans are primarily herbivores, feeding on aquatic plants, algae, and grasses. Their ability to swim, dive, and fly makes them versatile and adaptable birds.
5. Pelicans
Pelicans are large, water-loving birds known for their dramatic diving behavior. With their distinctive long bills and large throat pouches, pelicans dive into the water to catch fish. They use their webbed feet and strong wings to maneuver through the water, and their ability to dive from significant heights allows them to catch fish with precision. Pelicans are often found along coastal shores and are skilled swimmers and divers.
6. Loons
Loons are medium-sized birds with striking black-and-white plumage and a reputation for their excellent swimming and diving abilities. They are found in North America and Northern Europe, typically in freshwater lakes and cold regions. Loons are superb divers and can stay underwater for long periods of time as they search for fish and other prey. Their webbed feet are powerful, helping them propel through the water with ease. Loons also have a unique, haunting call that is often associated with serene, isolated lakes.
The Role of Fortunate Swimming Birds in Ecosystems
Fortunate swimming birds play an essential role in maintaining the health of aquatic ecosystems. As skilled predators, they help control populations of fish and invertebrates, ensuring that these species do not become overabundant and disrupt the balance of the ecosystem. Additionally, these birds often serve as indicators of water quality, as they are sensitive to changes in their environment.
For example, cormorants and pelicans can indicate the health of fish populations in coastal or freshwater ecosystems. If these birds are thriving, it is often a sign that the fish population is stable and healthy. Conversely, if these birds begin to struggle or disappear, it could indicate environmental issues such as pollution, habitat destruction, or a decrease in food availability.
Conservation Efforts for Fortunate Swimming Birds
While many swimming birds are well-adapted to their environments, they face several threats due to human activity. Habitat destruction, pollution, climate change, and overfishing can all impact the populations of aquatic birds. For instance, penguins are particularly vulnerable to climate change, as rising temperatures affect the availability of food and suitable breeding grounds.
Conservation efforts are crucial to ensuring the survival of fortunate swimming birds. Protecting wetland habitats, reducing plastic pollution in oceans, and creating marine reserves can help support the health of these birds and their ecosystems. Additionally, efforts to mitigate climate change, such as reducing carbon emissions, can help preserve the habitats of swimming birds in the long term.
Conclusion
A fortunate swimming bird is a remarkable creature that thrives in both aquatic and aerial environments. With their specialized adaptations, these birds are not only capable swimmers but also play an important role in the health of their ecosystems. From the graceful swan to the dynamic penguin, swimming birds display incredible abilities to survive and thrive in diverse habitats. However, as with many species, they face challenges in an increasingly changing world, making conservation efforts vital to their survival.
Whether you’re watching a duck paddle across a pond, observing a pelican dive for fish, or marveling at the agility of a penguin, fortunate swimming birds remind us of the beauty and resilience of nature. Their ability to navigate both water and air serves as a testament to the wonders of evolution and the adaptability of life on Earth.
GENERAL
Best Used Skidsteers With High Resale Value
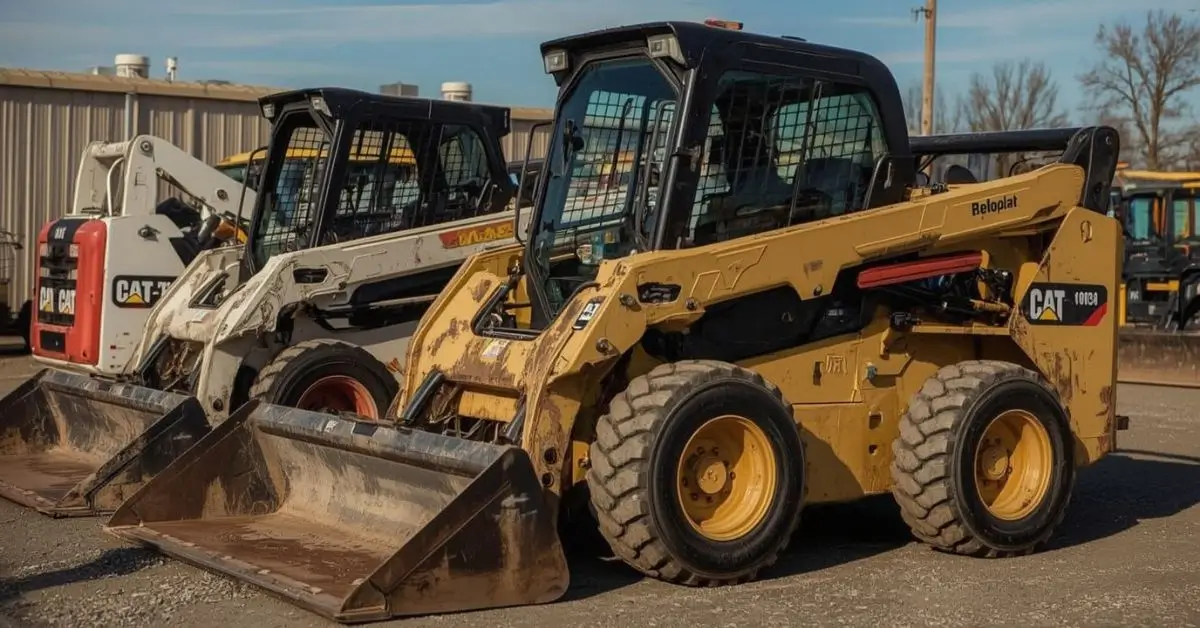

The biggest reason operators choose the best used skidsteers is simple: price. A brand-new model can cost between $40,000 and $70,000. Meanwhile, a quality second-hand machine with fewer than 2,000 operating hours can be half that cost, yet still deliver years of service.
Faster ROI
Contractors often highlight that investing in affordable skid steer loaders means hitting profitability sooner. Since skid steers are used across construction, landscaping, agriculture, and snow removal, they can generate returns quickly.
Sustainability Factor
In today’s eco-conscious market, buying used equipment also aligns with sustainability goals. Extending the lifespan of compact construction equipment reduces manufacturing demand and waste.
What to Look For in the Best Used Skidsteers
Engine Hours and Condition
Unlike cars, skid steers are valued more by engine hours than miles. Ideally, you want under 3,000 hours for a reliable machine. Always ask for service records before purchasing.
Attachments and Versatility
Don’t just focus on the base machine—skid steer attachments used can add enormous value. From augers to snowblowers, attachments turn your skid steer into a multi-purpose tool.
Maintenance History
A machine with documented oil changes, hydraulic checks, and regular inspections is far more reliable than one with a shiny coat of paint but no paperwork.
Comparing the Big Names: Caterpillar, Bobcat, and John Deere
Caterpillar Used Skid Steer
Caterpillar (Cat) is known for durability and strong resale value. Buying a Caterpillar used skid steer means access to one of the best dealer networks for service and parts.
Bobcat Skid Steer Deals
Bobcat practically invented the skid steer. If you’re scanning for Bobcat skid steer deals, you’ll find plenty of compact models favored by landscapers. They’re easy to maintain and often come with widely available attachments.
John Deere Skid Steer Loaders
For those loyal to green and yellow, John Deere skid steer loaders deliver strong lifting power and are favored in agricultural settings. They also hold value well in the heavy machinery resale value market.
Real-Life Example
A landscaping business owner shared online:
“I bought a 2018 Bobcat S570 with 1,800 hours for $24K. It’s been a workhorse—grading, hauling, and snow removal. I saved nearly $20K compared to new, and it’s paid itself off in under two years.”
This is a classic case of how the best used skidsteers can transform ROI for small business owners.
Pros and Cons of Buying Used
Pros
- Lower upfront cost
- Faster ROI
- Wide availability of second-hand skid steer reviews online
- Access to attachments at discounted rates
Cons
- Higher risk of hidden wear and tear
- Shorter lifespan compared to new
- May require immediate maintenance
- Limited or no warranty
Where to Find the Best Used Skidsteers
Dealerships – Certified pre-owned with service records
Auction Sites – Competitive pricing, but higher risk
Equipment Rental Companies – Well-maintained fleets often sold after a few years
Peer-to-Peer Platforms – Direct from owners, but requires careful inspection
Financing Used Skid Steers in 2025
One of the top questions buyers ask is about financing used skid steers. The good news? Many lenders now finance used equipment up to 10 years old. Look for flexible repayment plans, especially if you’re a small business owner balancing seasonal income.
Maximizing Heavy Machinery Resale Value
If you plan to resell your machine later, focus on brands with strong reputations. Keeping records of repairs and updates, and investing in popular skid steer attachments used, can significantly boost resale value.
Second-Hand Skid Steer Reviews: What Buyers Say
Online reviews are a goldmine. Most users agree:
Caterpillar holds value best.
Bobcat is easiest to service.
John Deere excels in farming applications.
Skid Steer Attachments: The Hidden Value
From pallet forks to brush cutters, attachments can double or triple the functionality of your machine. Buying them used can save thousands, especially if bundled with the loader.
FAQs
How many hours is too many for a used skid steer?
Anything beyond 4,000 hours typically requires careful inspection. Always compare second-hand skid steer reviews before committing.
What’s the difference between a Bobcat and Caterpillar skid steer?
Bobcat leads in compact models and affordable skid steer loaders, while Caterpillar focuses on durability and heavy machinery resale value.
Can I get financing for a used skid steer?
Yes! Many banks and online lenders now offer financing used skid steers, especially for small businesses with stable cash flow.
Are used skid steer attachments worth buying?
Absolutely. Quality skid steer attachments used can last for years and drastically expand your equipment’s functionality.
Conclusion
Finding the best used skidsteers in 2025 doesn’t have to feel overwhelming. With a clear understanding of brand differences, proper inspection checklists, and knowledge of financing options, you can make a smart, budget-friendly investment.
GENERAL
How to Choose the Best Trash Houston Service
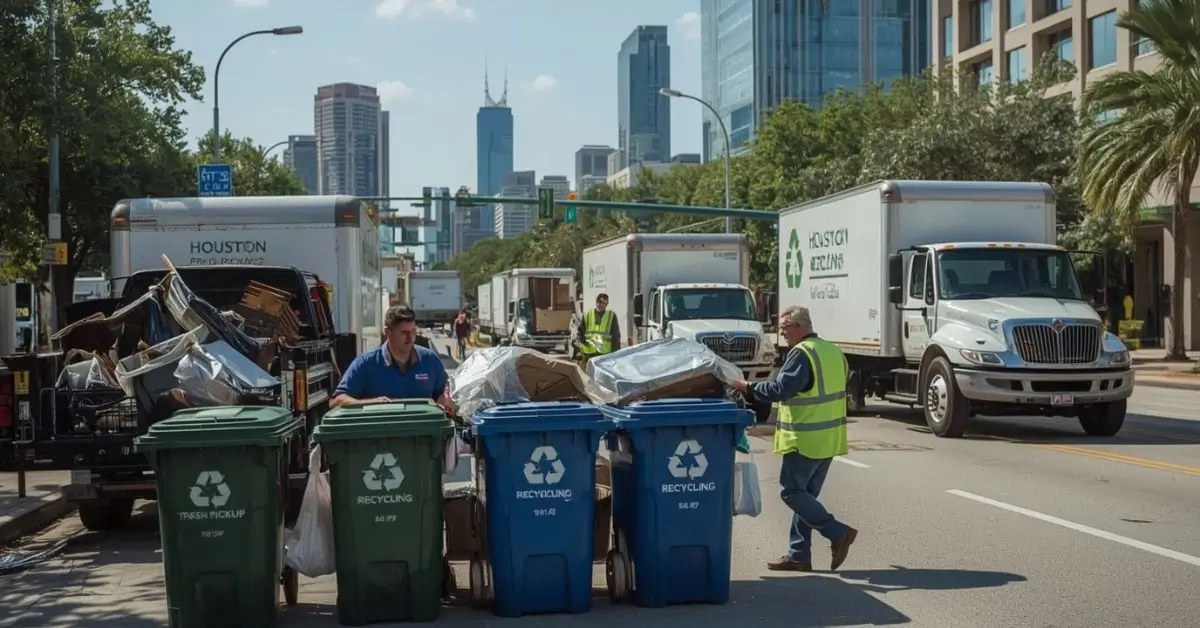

Finding the best trash Houston services can feel overwhelming in 2025. With so many providers offering different prices, pickup schedules, and eco-friendly options, how do you know which one fits your needs? Whether you’re a homeowner with weekly garbage, a renter managing bulky furniture, or a business needing dependable waste solutions, having the right trash service is essential.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know: from Houston junk removal and trash pickup services to eco-conscious recycling programs, pricing, and real customer insights. By the end, you’ll know exactly how to choose the best provider for your lifestyle and budget.
Why Choosing the Best Trash Service in Houston Matters
Living in Houston means dealing with city-sized trash challenges. With over 2.3 million residents, waste piles up quickly. If your trash doesn’t get picked up on time, you’re left with overflowing bins, unpleasant odors, and even potential pest problems.
On the other hand, the right provider keeps your home or business clean, saves you money, and—if you care about the environment—offers sustainable disposal methods. So the real question isn’t just about trash pickup; it’s about convenience, reliability, and community health.
Houston Junk Removal: Quick and Efficient Solutions
Sometimes, your weekly trash bin just won’t cut it. Maybe you’re remodeling your kitchen or finally getting rid of that old sectional sofa. That’s where Houston junk removal services step in.
These companies specialize in hauling away bulky items like furniture, appliances, yard debris, and even construction waste. Most offer same-day or next-day service, making them a lifesaver during moves or renovations.
Example: One Houston resident shared online, “I had a garage full of old furniture. The junk removal crew showed up within two hours and cleared everything in under 30 minutes. Worth every penny.”
Houston Trash Pickup Services: Staying on Schedule
The backbone of waste management in the city is Houston trash pickup services. Residential neighborhoods rely on scheduled pickups, usually once or twice a week, depending on the service plan.
Private companies often provide additional flexibility compared to city services, such as evening pickups, weekend schedules, or customized routes for HOAs. For busy households, that flexibility can be a game-changer.
Best Garbage Collection Houston: Who Stands Out in 2025?
When it comes to the best garbage collection Houston has to offer, competition is fierce. Providers now differentiate themselves through reliability, digital convenience (mobile apps for scheduling pickups), and sustainable practices.
Here’s a quick comparison table of top-rated options:
| Company | Services Offered | Average Cost (per month) | Eco-Friendly Options | Customer Rating (2025) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Waste Management Houston | Weekly trash, recycling, bulk pickup | $35–$50 | Yes | 4.5/5 |
| Texas Pride Disposal | Residential & commercial trash | $25–$40 | Limited | 4.3/5 |
| Junk King Houston | Junk removal, bulky items | $75–$200 (per job) | Yes | 4.7/5 |
| Republic Services | Trash, recycling, bulk, commercial | $30–$45 | Yes | 4.4/5 |
| Local EcoHaul | Junk removal, composting | $60–$150 (per job) | 100% | 4.8/5 |
Affordable Trash Removal Houston: Balancing Cost and Quality
Price matters. Many households in Houston want affordable trash removal Houston services without sacrificing reliability.
The good news? Plenty of local providers compete by offering competitive monthly rates, bundled recycling, or pay-as-you-go junk hauling. But beware: the cheapest option isn’t always the best. Delayed pickups or hidden fees can make budget choices more expensive in the long run.
Houston Waste Management Companies: Who to Trust
Choosing among Houston waste management companies comes down to reputation and customer service. The biggest names like Waste Management and Republic Services dominate the market, but smaller local firms often provide more personalized care.
In 2025, many companies have apps for tracking pickup schedules, digital invoices, and even live customer chat support—features that customers appreciate more than ever.
Trash Hauling Services Houston: Beyond Weekly Pickup
Not everything fits neatly into a trash bin. Trash hauling services Houston providers handle large-scale waste: construction debris, estate cleanouts, and event cleanups.
For example, if you’re a contractor renovating homes, you’ll likely need roll-off dumpsters or frequent hauling services. These providers tailor solutions for businesses and large households that generate more waste than average.
Bulk Trash Pickup Houston: Handling the Big Stuff
City services typically offer bulk trash pickup Houston on specific days each month. This covers items like mattresses, appliances, and yard waste.
But if you miss the city’s schedule, private companies can fill the gap. Many residents book same-day pickups for old furniture or appliances to avoid clutter piling up.
Eco-Friendly Junk Removal Houston: Going Green in 2025
Environmental awareness is growing, and eco-friendly junk removal Houston services are thriving. Instead of sending everything to landfills, these companies recycle, donate, or compost as much as possible.
Some even partner with local charities to give usable furniture or electronics a second life—great for both sustainability and community support.
Houston Recycling and Trash Services: Double Duty
Most households now look for combined Houston recycling and trash services. Bundling these services saves time, money, and stress.
Many companies now offer smart recycling bins that track your usage and reward you with points or discounts for consistent recycling efforts. It’s a win-win for customers and the environment.
Residential Trash Pickup Houston: Neighborhood Essentials
For families, residential trash pickup Houston is the most critical service. Reliable weekly collection keeps communities clean, prevents pests, and ensures compliance with city ordinances.
Private providers may offer customizable bin sizes, flexible schedules, and bundled recycling to fit different household needs.
Pros and Cons of Trash Services in Houston
Like any service, Houston’s trash providers come with trade-offs:
Pros:
Wide range of providers and price options.
Eco-friendly disposal methods are growing.
Technology makes scheduling and tracking easier.
Cons:
Cheaper providers sometimes delay pickups.
City bulk pickup schedules can be inflexible.
Hidden fees may surprise customers.
Expert Tips for Choosing the Best Trash Houston Service
Compare plans — Look at monthly costs, included recycling, and pickup frequency.
Check reviews — Customer experiences highlight reliability and hidden issues.
Ask about sustainability — Eco-friendly services may align better with your values.
Know your waste volume — Larger households might need bigger bins or more frequent pickups.
Confirm hidden fees — Always ask about fuel surcharges, bulky item charges, or missed pickup fees.
Real-Life Example: A Houston Family’s Experience
One family in The Heights shared their struggle: after months of missed pickups, they switched from a budget service to a mid-range provider. They paid $10 more per month, but their trash and recycling were finally collected on time. For them, peace of mind outweighed saving a few dollars.
FAQ’s
What is the most reliable trash service in Houston?
Top-rated companies like Waste Management and Junk King often score highest for reliability, but local eco-friendly providers also excel.
How much does trash removal cost in Houston?
Residential trash pickup usually ranges from $25–$50 per month. Junk removal and hauling services cost $75–$200 per job, depending on load size.
Does Houston offer free bulk trash pickup?
Yes, the City of Houston schedules free bulk trash collection monthly, but private providers can handle off-schedule pickups for a fee.
What are the most eco-friendly trash services in Houston?
Companies like Local EcoHaul and Junk King focus on recycling and donations, ensuring minimal andfill impact.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the best trash Houston service in 2025 comes down to matching your lifestyle, budget, and values with the right provider. Whether you want affordability, sustainability, or simply reliable weekly pickup, there’s a service tailored to your needs.
GENERAL
Prayer for Healing: The Powerful Path to Lasting Hope and Renewal

In life, pain and uncertainty are inevitable. Whether it’s illness, emotional wounds, or even spiritual dryness, we all face moments where medicine, positive thinking, or practical efforts just don’t feel like enough. That’s when many reach for something deeper—prayer for healing. Across cultures and traditions, prayer has been a vital tool for those seeking physical relief, emotional peace, and spiritual renewal.
But let’s be honest: people often wonder, Does prayer for healing really work? Or is it just a comforting ritual? This long-form guide dives deep—through history, faith traditions, psychological findings, and real-life examples—to explore why prayers for healing continue to matter in 2025 more than ever before.
Why We Seek Prayer for Healing
Humans crave meaning in suffering. Facing illness or heartbreak, many don’t just want treatment; they want hope and inner strength. Prayers for healing provide three key things:
- Comfort in chaos – A reminder that we’re not carrying our pain alone.
- A sense of control – Even when medicine runs out of options, prayer empowers us to take spiritual action.
- Community support – Shared prayers can unite families, friends, and ministries around a single healing intention.
Someone once shared online: “When I was at my lowest, my grandmother’s prayer for healing meant more than the doctor’s words. It gave me the strength to keep going.”
The Power of Healing Scriptures
In many religious traditions, turning to healing scriptures provides spiritual guidance. Believers often meditate on verses that promise relief, hope, or divine strength. For example, passages about resilience, encouragement, or God’s compassion become anchors in tough times.
Scripture serves two purposes:
- Faith Activation – Repetition reinforces trust and hope.
- Mental Peace – Comforting words quiet anxiety and bring rest.
Modern research in 2025 even shows that ritual reading of texts, affirmations, or prayer-like practices lowers stress hormones, supporting the body’s resilience.
Different Types of Prayers for Healing
Not all prayers for healing look the same. Here are some categories people use around the world:
1. Physical Healing
Asking for recovery from sickness, surgery, or chronic conditions. This is the most familiar form.
2. Emotional Healing
Addressing trauma, grief, or mental health challenges. Healing here means peace, not always cure.
3. Spiritual Healing
Seeking a renewed sense of purpose, forgiveness, or connection with God or a higher power.
4. Intercessory Healing Prayer
When one person prays on behalf of another—like families supporting a sick member.
5. Group or Community Prayer
Collective energy can be profound. In churches, mosques, synagogues, and even Zoom prayer groups, people unite for strength.
Does Prayer for Healing Really Work?
This is the million-dollar question. Studies on prayer are notoriously challenging, because how do you measure faith or its impact?
However, science does highlight some fascinating aspects:
- Placebo Effect: Believing in healing can trigger real improvements in pain perception and recovery.
- Stress Relief: Prayer reduces fight-or-flight responses, lowering blood pressure and boosting the immune system.
- Social Bonding: Being prayed for feels supportive, reducing feelings of loneliness and despair.
That doesn’t mean prayer replaces medicine—it complements it. A grounded approach is: Take your medication, follow the doctor’s plan, and pray for healing as part of holistic well-being.
A Real-Life Story of Healing
Consider the story of a professional who was battling burnout and anxiety. Traditional therapy helped but didn’t fully soothe her distress. She began practicing nightly meditation combined with her grandmother’s prayer for healing rituals. Slowly, her sleep improved, stress lessened, and she regained balance.
She described it this way: “I can’t prove prayer alone healed me, but I know I wouldn’t have survived without it.”
This kind of testimony resonates globally because healing isn’t always about a miracle—it’s about regaining strength to keep living fully.
Healing Scriptures That Bring Hope
Throughout centuries, millions have leaned on healing scriptures to inspire courage. These sacred texts are cited in bedside whispers, hospital rooms, and meditation circles. They often highlight themes like:
- God’s promise of renewal
- Strength in weakness
- Light in dark valleys
- Hope for restoration
Even for those not traditionally religious, reading inspiring wisdom passages fosters resilience, hope, and peace of mind.
The Modern Use of Prayers for Healing
In 2025, “prayer” doesn’t always look like folded hands in a pew. It might appear as:
- Mindfulness Prayers: Blending meditation and prayer language.
- Digital Prayer Circles: WhatsApp or Facebook groups uniting for an intention.
- Healing Journeys: Combining yoga, affirmations, and prayer.
- Holistic Medicine Integration: Doctors recognizing spiritual care as part of recovery.
This flexibility ensures prayer for healing stays alive in contemporary culture—it adapts to people’s needs without losing its essence.
The Dual Nature of Healing Prayer
Prayer has two dimensions:
- Petitionary Prayer – Asking God or a Higher Power to intervene.
- Transformative Prayer – Seeking strength to endure difficulty with grace.
Even when physical healing doesn’t happen, transformative prayer provides endurance, peace, and resilience.
Challenges and Misconceptions
- “If it doesn’t work, does that mean my faith is weak?” Absolutely not. Healing can manifest in unexpected ways—sometimes peace matters more than cure.
- “Can prayer replace medical treatment?” No. Responsible spiritual practice works alongside professional care.
- “Is prayer only for believers?” No. “Prayer” can be adapted as focused intention, meditation, or energy alignment across spiritual paths.
FAQs
1. What is a good short prayer for healing?
A good prayer is honest and heartfelt, such as asking for strength, peace, and restoration—spoken in your own words.
2. Can prayer actually heal physical illness?
Prayer may not directly cure disease, but it can reduce stress, improve outlook, and complement medical care, supporting overall healing.
3. What healing scriptures are often used in prayer?
Passages that emphasize strength, renewal, and hope are most frequently chosen during illness or hardship.
4. Is there a difference between prayers for healing and affirmations?
Yes, affirmations are self-directed statements, while prayers for healing are directed toward God or a higher power. Both can coexist.
Final Thoughts
At its heart, prayer for healing isn’t about magical words—it’s about intention, hope, and connection. In 2025, amidst constant stress and global challenges, people are rediscovering the power of pausing, centering themselves, and speaking words of faith.
Whether through ancient healing scriptures, whispered prayers for healing, or modern meditation practices, the goal remains the same: to find restoration of body, mind, and soul.
-

 GENERAL9 months ago
GENERAL9 months agoClassroom6x: Revolutionizing the Future of Learning
-

 ENTERTAINMENT9 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT9 months agoUnveiling the Mystery of Kashito_Toto: A Digital Frontier
-

 TECHNOLOGY9 months ago
TECHNOLOGY9 months agoUnlocking the Mystery of Vy6ys: A Hidden Gem
-

 TECHNOLOGY9 months ago
TECHNOLOGY9 months agoUnlocking the Power of SSIS 816: A New Era in Data Integration
-

 GENERAL9 months ago
GENERAL9 months agoQuid Pro Quo Harassment: What It Is and Why It Matters
-

 GENERAL9 months ago
GENERAL9 months agoUnraveling Time: What Hour Was It 8 Hours Ago?
-
 BUSNIESS9 months ago
BUSNIESS9 months agoUnderstanding Sell in Trade Locker: A Key to Smart Trading
-

 HEALTH9 months ago
HEALTH9 months agoKingymab: Redefining Fitness and Wellness Excellence
