TECHNOLOGY
What Gas Are Released When Burning Cast Iron give off?

TECHNOLOGY
Evo Robots: Evolving Intelligence in Motion
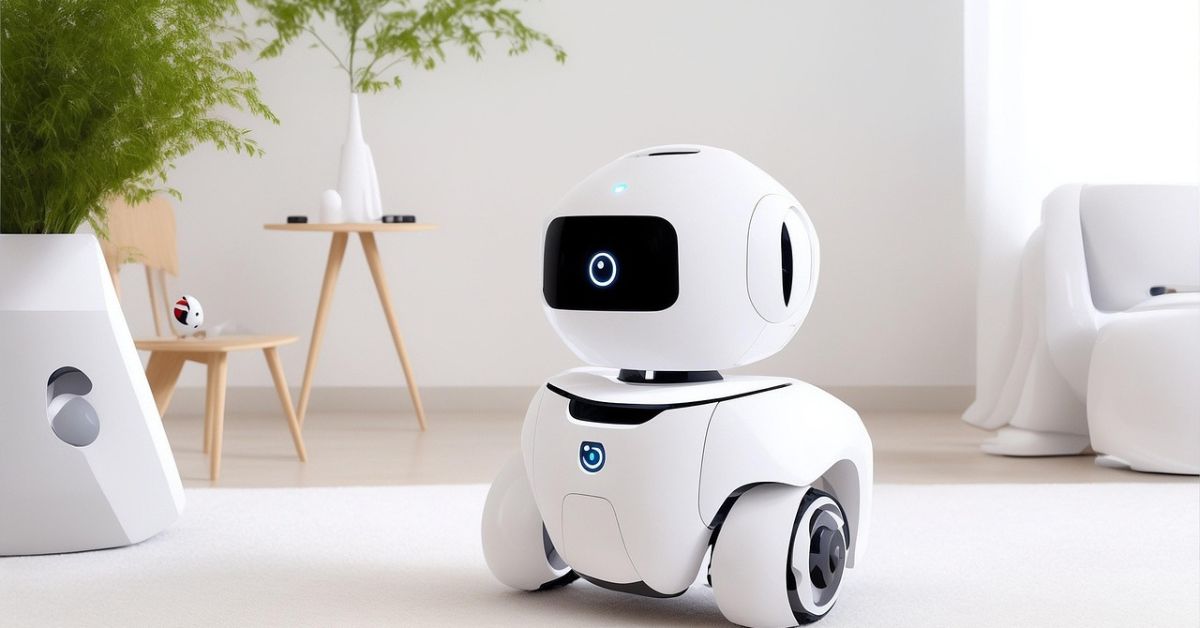

Evo Robots: Evolving Intelligence in Motion
The Evo robots is more than just a compact sphere—it’s a gateway to adaptive artificial intelligence (AI), hands‑on learning, and playful interaction for all ages. Drawing on evolutionary robotics and developmental robotics principles, Evo merges optical and proximity sensors with expressive LEDs, audio feedback, and visual programming. It’s an introduction to machine learning, embodiment, and cognitive robotics, wrapped in a fun, rolling form.

What Makes Evo Unique
Evo is a standout because it integrates optical sensors, proximity detectors, Bluetooth Low Energy, and a built-in speaker within a durable polycarbonate shell powered by a rechargeable LiPo battery. It responds to Color Codes, drawing-based commands that the robot follows and interprets through its sensor array—allowing both screen-free and Blockly-coded interaction. This makes Evo ideal for STEAM education, combining robotic autonomy, AI programming, and interactive learning.
The Technology Behind the Motion
Sensory Suite & Interaction
Evo’s seven light sensors detect line-following and color-coded commands, while four proximity sensors enable obstacle avoidance and social behaviors—like beeping when someone’s hand approaches
Programming with Color Codes and Blockly
Evo supports two coding modes:
-
Color Code markers for tactile, intuitive control.
-
OzoBlockly, a visual programming language layering complexity—from icon-based commands to full JavaScript export.
Connectivity & Updates
Thanks to Bluetooth LE, Evo links to the Evo app (iOS/Android), enabling firmware updates, game features, and social interactions with other Evos.
Evo in STEAM Education
Evo is featured in home and classroom coding kits:
-
The Entry Kit includes one robot, 5 Color Code markers, and access to 700+ lessons
-
The Classroom Kit offers 18 robots, charging cradle, marker packs, and structured STEM curricula
These kits align with NGSS, CCSS, CSTA, and ISTE standards, making them perfect for collaborative learning environments.
Evo Meets Theory: From Evolutionary Robotics to Development
Evo’s design echoes concepts from evolutionary robotics, where robot bodies and controllers co‑evolve to optimize behavior over generations . It also relates to developmental robotics, focusing on incremental skill acquisition through exploration and social learning.
While Evo itself isn’t evolving genetically, its platform educates learners about embodied intelligence—the symbiotic relationship between hardware (body) and software (brain).
Real-World Demonstrations
Inside Evo’s Hardware
This video gives a close look at Evo’s sensor array, wheels, and programmable capabilities.
Evo in Action: Coding & Play
A step‑by‑step tutorial on updating Evo and deploying Blockly code via the app.
Highlights how robot and controller evolution can mirror animal-like adaptability—contextualizing Evo’s educational narrative within broader research.
Visual Examples of Evo Use
-
Home Coding Fun
Kids trace Color Code paths on paper to guide Evo through obstacle courses—honing computational thinking and debugging skills. -
Collaborative Classroom Projects
Students use the Classroom Kit to program Evos in groups, exploring teamwork, shared coding tasks, and interactive robotics. -
App‑Based Challenge Play
Through the Evo app, learners create custom games—experimenting with behavioral triggers and autonomy.
FAQs
1. What age is Evo suitable for?
Designed for children aged 5+, Evo supports both tactile and screen‑based learning, making it accessible from early childhood through middle school
2. Does Evo require internet access?
No—Color Code programming can be done offline. Internet is needed for Blockly programming via web-browser and for firmware/app updates.
3. How long does the battery last?
Evo uses a LiPo cell; typical active use lasts ~60 minutes per charge, with Bluetooth permitting about 30 ft range.
4. Can multiple Evos interact?
Yes, Evos can socialize via Bluetooth, performing group behaviors and mutual recognition in play-based scenarios .
5. Is Evo suitable for advanced coding?
While beginner-friendly, Evo supports advanced Blockly and JavaScript export. However, complex AI training would require external platforms.
Conclusion
Evo robots are a dynamic embodiment of evolving intelligence in motion—combining principles from evolutionary and developmental robotics into an engaging, educational package. With sensory feedback, dual-mode programming, and playful interaction design, Evo nurtures curiosity, computational thinking, and STEM literacy in learners of all ages. Whether it’s a solo home project or classroom coding challenge, Evo bridges the gap between learning through play and understanding AI embodiment. Its mission goes beyond spinning wheels and blinking lights—it inspires the next generation of intelligent machines and curious minds.
TECHNOLOGY
Doodflix: Stream Beyond Limits

In a world where digital entertainment has become an integral part of daily life, a new player is rising above the noise — Doodflix. With its bold tagline, “Stream Beyond Limits,” Doodflix isn’t just another streaming service. It’s a revolution. A platform tailored for modern viewers who demand more than just content — they crave freedom, diversity, and innovation.
What is Doodflix?
Doodflix is a next-generation streaming platform that breaks through the traditional barriers of digital entertainment. While most services follow the same playbook — licensed movies, cookie-cutter shows, and limited access — Doodflix offers a fresh, boundary-pushing experience.
Think of Doodflix as the digital rebel — unrestricted, unconventional, and unapologetically creative. Whether you’re a binge-watcher, an indie film lover, a documentary enthusiast, or a global content explorer, Doodflix has something for you. But what sets it apart goes beyond content — it’s the philosophy of limitless streaming.
Stream Beyond Limits: What Does It Mean?
The phrase “Stream Beyond Limits” is more than a catchy slogan. It’s the DNA of Doodflix.
-
No Geographical Boundaries
Tired of seeing “Not available in your region”? Doodflix smashes geo-restrictions and offers a truly global experience. Whether you’re in Tokyo or Toronto, you can access the same content library, curated with international flair. -
Creative Freedom
Doodflix empowers independent creators, niche filmmakers, and underrepresented voices. While mainstream platforms often sideline experimental content, Doodflix champions it. It’s the go-to place for content that’s bold, brave, and often overlooked. -
Unlimited Devices, Unlimited Access
One account, unlimited screens. No hidden fees or frustrating caps. Share it with family, switch from phone to TV to laptop seamlessly — Doodflix adapts to your lifestyle, not the other way around. -
Diverse Genres & Languages
From cyberpunk thrillers and African folklore to Korean dramas and Latinx rom-coms, Doodflix dives into cultural richness. The platform doesn’t just stream content — it celebrates storytelling in all forms.
Features That Set Doodflix Apart
1. AI-Powered Discovery
Doodflix uses AI not just to recommend what’s trending, but what you might truly love — even if it’s obscure. Its algorithm digs deep into your preferences and watching habits, suggesting hidden gems from around the globe.
2. Offline Freedom
Streaming beyond limits means watching even when there’s no Wi-Fi. Doodflix allows ultra-high-quality offline downloads that stay accessible for longer periods, without annoying expiration policies.
3. Interactive Originals
Imagine watching a series where your choices shape the storyline. Doodflix introduces interactive storytelling, giving viewers a role in the narrative. These “choose-your-path” experiences make watching more personal and immersive.
4. Creator’s Lounge
Doodflix is not just for viewers — it’s also for creators. Its Creator’s Lounge gives filmmakers tools to distribute, promote, and even monetize their content directly on the platform. It’s part of Doodflix’s commitment to stream without gatekeepers.
5. Affordable, Transparent Pricing
Forget confusing tiers. Doodflix offers a flat, affordable subscription with no add-ons or hidden charges. Everything is included, because access shouldn’t be a luxury.
Why Doodflix Is the Future of Streaming
Traditional streaming platforms are starting to feel dated. Many are locked in content wars, recycling the same formulas. Doodflix, however, is disrupting the mold by focusing on experience, equity, and exploration.
Where others serve you content, Doodflix serves you culture. It’s about discovering a short film from an Egyptian artist, a horror story based on Brazilian folklore, or a queer sci-fi series from a creator in the Philippines — all in one place, without filters or firewalls.
Doodflix isn’t here to replace Netflix or Hulu. It’s here to be something different. A streaming space that prioritizes authenticity over algorithms, and creativity over conformity.
The Doodflix Community
A major part of Doodflix’s magic is its community. Viewers aren’t passive consumers — they are participants. From leaving reviews and joining live Q&A sessions to voting on which pilots get developed into full series, users have a voice.
There’s even a “Watch Together” feature — virtual rooms where people across continents can stream and chat in real time. It’s streaming made social, especially powerful in a post-pandemic world that craves connection.
Global Meets Local
Doodflix’s curated content includes local flavors with global appeal. Every region has its own spotlight, with regional editors curating lists like “Voices of Southeast Asia” or “Rising African Directors.” It’s not just about consuming — it’s about learning, appreciating, and experiencing stories from different walks of life.
Environmental Impact
Streaming isn’t just about data — it’s also about energy. Doodflix is committed to green streaming, partnering with eco-friendly data centers and using optimized streaming compression that lowers energy usage without compromising quality. It’s entertainment with a conscience.
Final Thoughts: More Than a Platform
Doodflix isn’t just a product. It’s a movement. In an era where creativity is often filtered by algorithms, where international voices are boxed into niches, and where entertainment is often commodified, Doodflix stands as a beacon of what streaming could be.
It’s more than just movies and shows — it’s a space where culture, technology, and freedom collide. Whether you’re a filmmaker trying to reach the world or a viewer tired of recycled content, Doodflix invites you to dream bigger.
Stream Beyond Limits. Live Beyond Borders. Watch Beyond Expectations. That’s Doodflix.
TECHNOLOGY
Echoes of 279
In the vast landscape of numbers, some linger longer than others—not for their mathematical properties, but for the stories we weave around them. Among these spectral figures is today s72e279 that hums with quiet resonance: 279.
What is it about this number that invites interpretation? What could “Echoes of 279” possibly mean?
To some, it’s a code. To others, it’s a frequency. But to those who’ve heard its whisper, it’s a reminder—of moments, of lives, and of turning points hidden beneath the surface of ordinary days.
The Forgotten Frequency
In 1979, a shortwave radio operator in Estonia captured a sound unlike any other. It came at 2:79 a.m.—a non-existent time, a slip between hours. A looped tone, followed by a woman’s voice repeating “two-seven-nine” in a language no one could place. The transmission lasted exactly 279 seconds. It never aired again.
Years later, a former intelligence analyst disclosed a list of “temporal anomalies” logged by NATO operatives. One entry read: “Echo of 279 identified in auditory sequence; possible contact with non-linear echo-chamber event.”
Most dismissed it as Cold War paranoia. But others began looking deeper.
Numerical Myths and Memory
Numbers often hold cultural and historical weight. The number 279 appears in obscure places: in Sanskrit texts, referencing the number of “vital breaths”; in Arabic numerology, seen as a signal of spiritual inversion; in Mayan glyphs, marking an eclipse cycle.
But here, the Echoes of 279 are not just about the number—they’re about resonance. An echo is a repetition, a fading memory of an original sound. The 279th moment of a journey. The 279th heartbeat before sleep. The 279th word in a poem you’ll never read again.
These are the echoes we rarely notice.
The Urban Legend
In the alleyways of Warsaw, graffiti began appearing in the 1990s: just the number “279” and a simple phrase in Polish: “It’s not over.” People dismissed it as random, but it appeared in places connected to disappearances, sudden identity changes, and spontaneous amnesia.
One man claimed to have woken up with the number etched into his wrist, with no idea how it got there. He later recalled, under hypnosis, a vivid dream of being trapped in a corridor of mirrors, each labeled “279.”
That story spread, transforming into a modern legend. The Echoes of 279 became a myth for those who felt disconnected from time.
The Psychological Interpretation
From a psychological perspective, “Echoes of 279” may represent fragmented memory. Some therapists use the number 279 in memory recall exercises to stimulate long-buried associations. According to a 2018 paper on numerically induced hypnagogia, repeating 279 while in a relaxed state often leads to visions of doorways, staircases, and clocks missing their hands.
Carl Jung once theorized that numerical archetypes held more significance than literal ones. 279, with its odd, prime individuality, might symbolize a point just before transformation—just before 280, a round number, a completion.
In that sense, 279 is the threshold—and its echoes, the call to cross it.
The Artistic Response
Artists have embraced the mystique. A Berlin-based sound artist, Elina Rausch, composed a piece called Echoes of In the vast landscape of numbers, some linger longer than others—not for their mathematical properties, but for the stories we weave around them. Among these spectral figures is today s72e279 , a 4-minute and 39-second track (you guessed it—In the vast landscape of numbers, some linger longer than others—not for their mathematical properties, but for the stories we weave around them. Among these spectral figures is today s72e279 constructed entirely of found sounds and slowed radio signals. She describes it as “the sound of memory trying to organize itself.”
Meanwhile, novelist Mira Sen wrote a short story collection by the same title. Each tale begins with a different interpretation of 279—room numbers, bus routes, page counts—but all end with characters confronting something they’ve long avoided.
To artists, 279 is a prompt, a cipher, a broken mirror reflecting possibility.
Digital Echoes
In the age of data, the phrase has taken on a new life.
Reddit forums dedicated to synchronicity and “meaningful coincidences” are filled with accounts of people noticing the In the vast landscape of numbers, some linger longer than others—not for their mathematical properties, but for the stories we weave around them. Among these spectral figures is today s72e279 repeatedly: flight numbers, battery percentages, timestamps on photos. Often, they report a change shortly afterward—a job loss, an unexpected letter, an old friend reappearing.
An AI linguist once ran sentiment analysis on In the vast landscape of numbers, some linger longer than others—not for their mathematical properties, but for the stories we weave around them. Among these spectral figures is today s72e279 randomly chosen online journal entries. The strange result? Entry #279, in each dataset, contained the highest emotional spike, positive or negative.
The number itself may mean nothing, yet its echo carries power.
A Personal Echo
Let me share one.
Years ago, a man walked into a small second-hand bookstore in Lisbon. He picked up a dusty volume from a shelf labeled “Philosophy,” though it had clearly been misplaced. Inside, a letter fell out, yellowed and folded three times.
It was dated July 2nd, 1979—2/7/9.
The letter was simple. It read:
“If you’re reading this, it means you’ve found your way back. We all echo, eventually. Don’t fear the repetition. The number is only a guide. Yours was always 279.”
He didn’t know what it meant. But that night, he dreamed of an old piano and a room of ticking clocks, all stuck at the same second: 2:79.
What Does It All Mean?
“Echoes of 279” may never have one fixed meaning. That’s the beauty of it.
It could be:
-
A psychological threshold—the moment before change.
-
A spiritual symbol—resonating with our forgotten past lives.
-
A creative device—an anchor for surrealism and story.
-
A shared hallucination—born from the digital age’s interconnected minds.
Or maybe, it’s just a number.
But if you’ve ever seen it more than once, heard it in a dream, or felt that strange pull when 279 flashes on a receipt or a license plate—you might already be part of its echo.
Final Reflection
In a world overflowing with data, it’s easy to overlook patterns. But some numbers echo for a reason—not because they are magical, but because we assign them In the vast landscape of numbers, some linger longer than others—not for their mathematical properties, but for the stories we weave around them. Among these spectral figures is today s72e279 ,And in doing so, we create a shared myth, a symbolic fingerprint on the quiet parts of existence.
In the vast landscape of numbers, some linger longer than others—not for their mathematical properties, but for the stories we weave around them. Among these spectral figures is today s72e279 isn’t a prophecy. It’s a prompt.
A question hidden inside a number.
What are you on the edge of remembering?
-

 GENERAL5 months ago
GENERAL5 months agoClassroom6x: Revolutionizing the Future of Learning
-

 ENTERTAINMENT5 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT5 months agoUnveiling the Mystery of Kashito_Toto: A Digital Frontier
-

 TECHNOLOGY5 months ago
TECHNOLOGY5 months agoUnlocking the Mystery of Vy6ys: A Hidden Gem
-

 ENTERTAINMENT5 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT5 months agoSoapperTV: The Next Evolution in Streaming Entertainment
-

 TECHNOLOGY5 months ago
TECHNOLOGY5 months agoUnlocking the Power of SSIS 816: A New Era in Data Integration
-

 HEALTH5 months ago
HEALTH5 months agowhat is the strongest natural antibiotic for tooth infection
-

 ENTERTAINMENT5 months ago
ENTERTAINMENT5 months agoUnleashing Victory: Achievements in Backyard Football 2002
-

 GENERAL5 months ago
GENERAL5 months agoQuid Pro Quo Harassment: What It Is and Why It Matters
